Nutrition Simplified: 4 Easy Steps
Do you have goals to eat better, lose weight, or address a nagging health condition?
Most of us have goals related to our health, and many of those goals require changes to our nutrition. But, there is so much noise about how to eat well, it can be overwhelming!
So, to help you achieve your goals we’ve put together a simple list of 4 things to include with each meal that will set you up for success. This concept will streamline all your meal choices from here on out, and help you meet your goals. And it’s easy, we promise!
But first, a little background information…
Macronutrients
If we tell you that “macro” means large, the term “macronutrient” becomes fairly straightforward! Macronutrients, in short, are nutrients we need in large quantities.
Macronutrients include carbohydrates, proteins, fats, fibre, and water (although water intake is a topic for another article!).
The Standard North American Diet (SAD)
Unfortunately, the Standard North American Diet (SAD), tends to include large amounts of highly-processed foods usually simples carbohydrates loaded with sugar and additives which often results in low intake of protein and fibre. Imbalanced intake of macronutrients and consuming low-nutrient foods contributes to the development of many “diseases of civilization” such as heart disease (1), cancer (2), obesity, diabetes (3), digestive disorders (4), infertility, and mood disturbances including anxiety and depression (5).
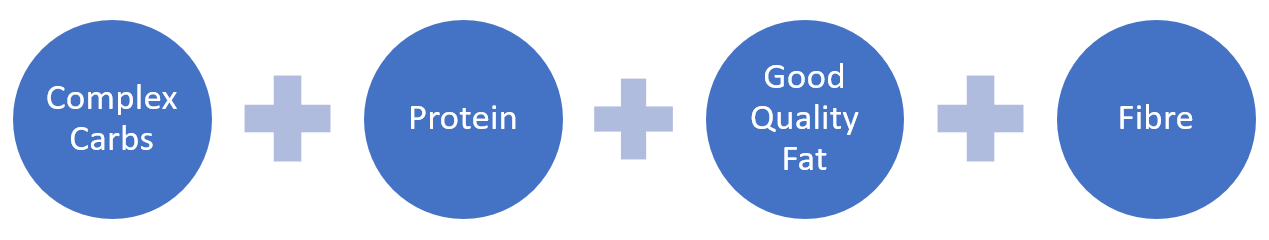
The Balanced Meal Equation
To create a balanced meal, you want to ensure you’re consuming each of the necessary macronutrients; which will naturally reduce glycemic load. Glycemic load is the measure of how quickly sugars enter your blood stream. The goal is to have gradual increases in blood sugar, with sustained energy over time; rather than the huge spikes and crashes caused by the SAD. To accomplish this, it’s as simple as 1, 2, 3, 4!
Keep reading and we’ll give you some ideas about how to implement this concept, as well as what benefits you’re likely to experience from consuming all the macronutrients at each meal.
Complex Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the body’s preferred source of energy. Carbohydrates are digested mainly in the mouth as enzymes in our saliva break down these compounds into sugars that our body uses for short bursts of energy. Complex carbohydrates include categories of foods such as vegetables (excluding potatoes and corn) and whole grains (not refined flours), as well as beans and legumes, which are a lesser-known source.
Proteins
Protein is used for building, repairing, and regenerating muscles; and also make up the structure of nearly all body tissues. Proteins are digested mainly in the stomach, and typically take between 2-4 hours to pass to the small intestine for further absorption. Animal based foods such as meat, poultry, or egg whites provide high quality proteins. There are many plant-based sources of proteins as well including nuts and seeds, beans and lentils, and pseudograins such as quinoa or amaranth.
Good Quality Fats
Fats don’t make us fat! Quite the opposite is true. Fats are a part of every cell membrane of our bodies, they make up the majority of our brain and eyes, assist in hormone production, and aid in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. Fats are digested within the small intestine. Healthy fats that come from things like olive oil, coconut oil, fish, hemp, flax and avocado are critical to support the brain, hormone function, and stabilize energy.
Fibre
Fibre is a macronutrient found in carbohydrate-rich foods. There are two main types of fibre – insoluble, which doesn’t dissolve in water, and soluble, that does. Both types of fibre support our digestive function by promoting regular bowel movements and providing important sources of food to the good bacteria living in our guts. Insoluble fibre acts like little brushes, sweeping food through the intestines, while soluble fibre acts like little sponges helping to absorb toxins within the digestive tract and carry them out of the body as waste.
Fibre is not digestible and passes through our digestive system intact. Vegetables are a preferred source of fibre, and ideally 50% of each meal should be based around various vegetables. Some other ideal sources of fibre include whole grains, beans and legumes, many seeds such as flax or chia, and berries.
But, What About Special Diets?
One of the biggest benefits to following this 4-step dietary guideline is that it applies to every human on the planet regardless of their dietary preferences, ancestry, religious affiliations, beliefs about animal welfare, or health conditions. Every single one of us needs to consume all four of these macronutrients.
Within this frame work, you are able (possibly with the assistance of a nutritionist or dietitian) to adjust the ratios of macronutrients at a more advanced level to work for your beliefs and preferences whether you’re following a ketogenic diet, are vegan or vegetarian, or anything in between.
But, for most individuals in North America, just having an awareness of these four macronutrients and including them all at each meal is a huge step in a positive direction!
Top 5 Health Benefits of Consuming All Macronutrients
Balanced Blood Sugar Levels
Blood sugar spikes caused by consuming refined carbohydrates such as white bread, white pasta and baked goods) and sugars, or meals with imbalanced macronutrients (for North Americans that typically due to meals lacking in protein and/or fibre) lead to an increased output of the hormone insulin (which is pro-inflammatory), along with other undesirable outcomes like further cravings, and rapidly changing blood sugar levels. A “blood sugar roller coaster” is the cause of many common symptoms including fatigue, dizziness, nervousness, and irritability. Because protein and fat are digested more slowly, and further down the digestive tract than carbohydrates, they help to regulate blood sugar levels by slowing the absorption of sugars into the blood. Staying off that blood sugar roller coaster helps protect against many chronic diseases including high cholesterol, heart disease, and high blood pressure.
Weight Loss
When macronutrient needs are well met satiety is increased, making you feel fuller longer. This can have positive impact on metabolic rate as well, increasing calorie burn without added exercise. By reducing glycemic load, the body is also required to produce smaller amounts of insulin to keep blood sugar levels at normal levels. Because insulin is our “fat storage hormone” supporting the body to naturally require and produce less insulin can benefit weight loss and weight management strategies greatly.
Improved Mood
When macronutrients are balanced at each meal, we have all the building blocks for happy hormones like serotonin and endorphins. Plus, we’ve all been “hangry”, right? Staying off that blood sugar roller coaster also means less blood sugar crashes that can lead to feeling anxious, depressed and irritable.
More Energy
A well-balanced diet means your body is better able to turn food into fuel, and that your cells communicate more effectively. When consuming balanced macronutrients energy levels tend to be higher and more stable.
Reduced Inflammation
A high-fibre diet can help reduce inflammation by modifying the pH in the gut, reducing gut permeability, and supporting our good bacteria. A diet including adequate amounts of all macronutrients also helps reduce inflammation because of lower insulin secretion. Although it serves many valuable biological purposes, in addition to being our “fat-storage hormone”, insulin is also pro-inflammatory.
How To Consume All Macronutrients At Each Meal
Here, we’re outlining some simple meal ideas that include complex carbohydrates, protein, good quality fats, and fibre just to get you started with imagining what these macronutrients would look like on your plate!
- Steel cut oats with ground flax seed and raw nuts
- Mixed green salad with chicken breast and olive oil vinaigrette
- Roast beef with root vegetables
- Shrimp and vegetable stir fry
- Smoothie with spinach, protein powder, MCT coconut oil, and chia
In Summary
This is not complicated, it’s as simple as can be! Improving our diets can start with increasing our individual and collective awareness of the macronutrients we require from our foods, and doing a little mental 4-point checklist at each meal to ensure we have our bases covered.
If you feel you would benefit from one-on-one support to move your diet to a more balanced state, please reach out or book an appointment, we’re here to help!
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3342583/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2866629/pdf/nihms-188521.pdf
- https://diabetesjournals.org/spectrum/article/21/3/160/2008/The-Pathophysiology-of-Cardiovascular-Disease-and
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6520976/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7322666/











